WAP to check whether input alphabet is a vowel or not?
The logic is simple, we know that alphabet has five vowel
( a,e,I,o,u).
Vowel={ a,e,I,o,u , A,E,I,O,U }
If user enters any
character from this set then it will be vowel. One thing we keep in mind that c
is case sensitive programming language so we have to consider both cases small
latter vowel( a,e,I,o,u) as well as capital latter vowel(A,E,I,O,U).C Program: By Using If-else method
#include#include void main() { clrscr(); char ch; printf("Enter any Character : \n") ; scanf("%c",&ch); if(ch=='a'||ch=='A'||ch=='e'||ch=='E'||ch=='i' ||ch=='I'||ch=='o'||ch=='O'||ch=='u'||ch=='U') { printf("entered character : %c is vowel!!\n",ch); } else { printf("entered character : %c is not vowel!!\n",ch); } getch(); }
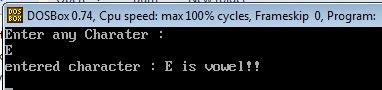
Output of c program:
Download c program
C Program (code): By Using Switch ()
#include#include void main() { clrscr(); char ch; printf("Enter any Character : \n"); scanf("%c",&ch); switch(ch) { case 'a': case 'A': case 'e': case 'E': case 'i': case 'I': case 'o': case 'O': case 'u': case 'U': printf("Entered character = %c is vowel!! ",ch); break; default: printf("Entered Character = %c is not vowel!!",ch); } getch();





No comments